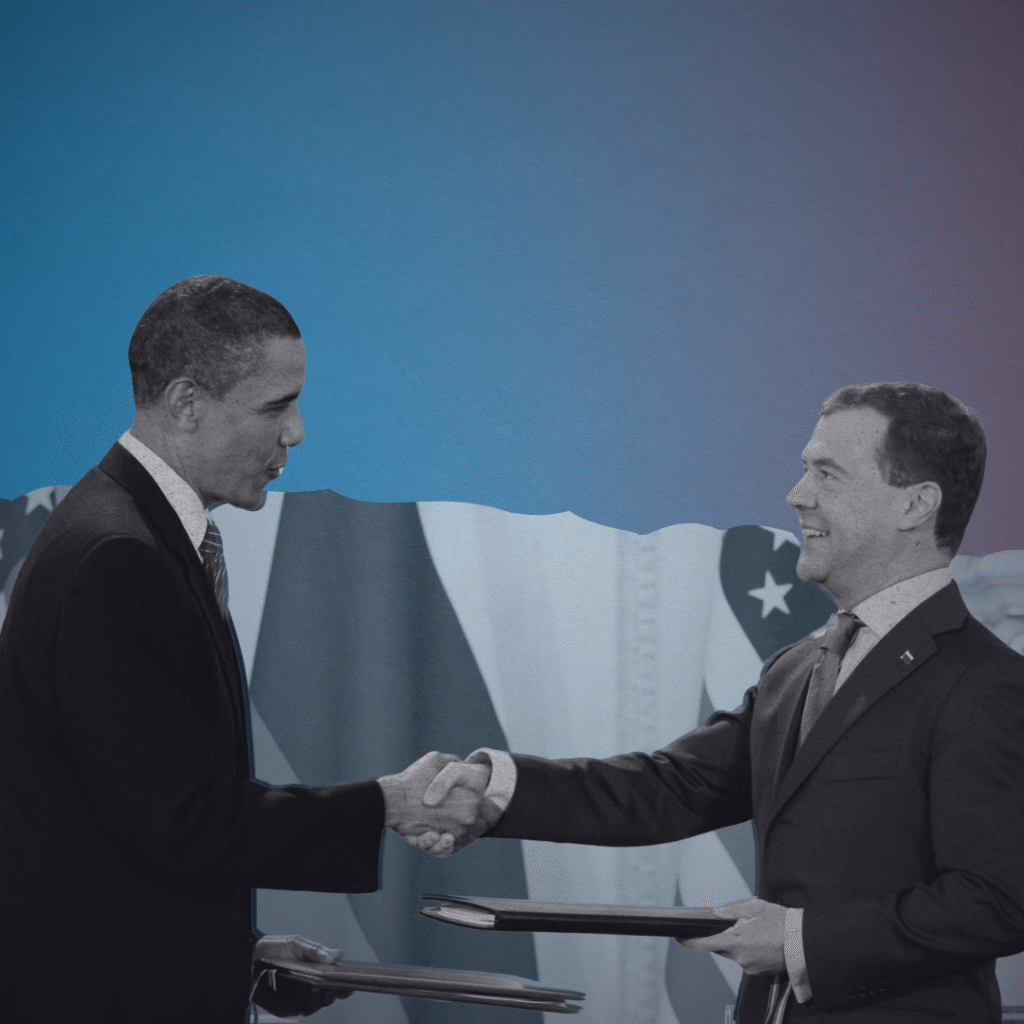
Story Center
Current news and exciting stories highlighting the good, the bad, and the truth about nuclear weapons in the world.
Please contact Ploughshares' Communications Manager Rebecka Green at rgreen@ploughshares.org for further information on any of these stories or to pitch topics and interviews.